Recognizing Separation Anxiety and Its Symptoms
Separation anxiety is characterized by excessive and persistent fear and anxiety (inadequate for the stage of development). It is related to separation from attachment figures.
Intense separation anxiety from close people is a characteristic of healthy early development. It occurs around the age of one year and may indicate the result of a secure attachment relationship.
The symptoms of a separation anxiety disorder or elements of this clinical picture, as presented in the Diagnostic Manual of Mental Disorders, are:
- Recurring excessive discomfort related to the separation from close people, which can be experienced or anticipated;
- Persistent and excessive concern regarding the loss of attachment figures or the possibility that they may suffer from illness, injury, disaster, or death;
- Nightmares with separation themes;
- Repeated somatic attacks: headaches, nausea, vomiting, and stomach pain when separation or anticipation is involved.
In adults, a separation anxiety disorder can limit the ability to adapt to changes in circumstances (changing residence or marriage). As parents, adults who show these symptoms can be overly concerned about their children or partners and feel significant discomfort when separated. There is also a constant need to check where the close people are.
Separation anxiety can develop after a stressful period following a loss (death of a relative or pet), an illness in the individual or a close person, moving to a new area, etc.
In young adults, among the factors that could trigger separation anxiety are leaving the parental home, beginning of a romantic relationship, and becoming a parent. Thus, overprotection and an intrusive relationship with the partner and/or child may be associated with separation anxiety.
Sometimes adults who experience these symptoms tend to limit their independent activities outside the home or in the absence of the people they are attached to. They also show dependence on essential people, nostalgia, and discomfort to the point of pain when they are away from home. These tendencies create sources of frustration for the family due to excessive demands.
Physical symptoms include depression, palpitations, dizziness, and fainting sensation.
Managing Separation Anxiety and Boosting Self-Confidence

Experiencing these symptoms for more than six months can cause clinical discomfort in several environments where the person is active. In this case, a specialized consultation with a psychiatrist, a clinical psychologist, and a psychotherapist is necessary. Of course, some people experience the entire clinical picture above or only specific symptoms of this disorder. In the first case, a diagnosis can be made; in the second case, it cannot.
When we are following the symptomatology of separation anxiety, assessing the intensity of the symptoms is essential. In most cases, time and intensity can indicate the severity of the discomfort.
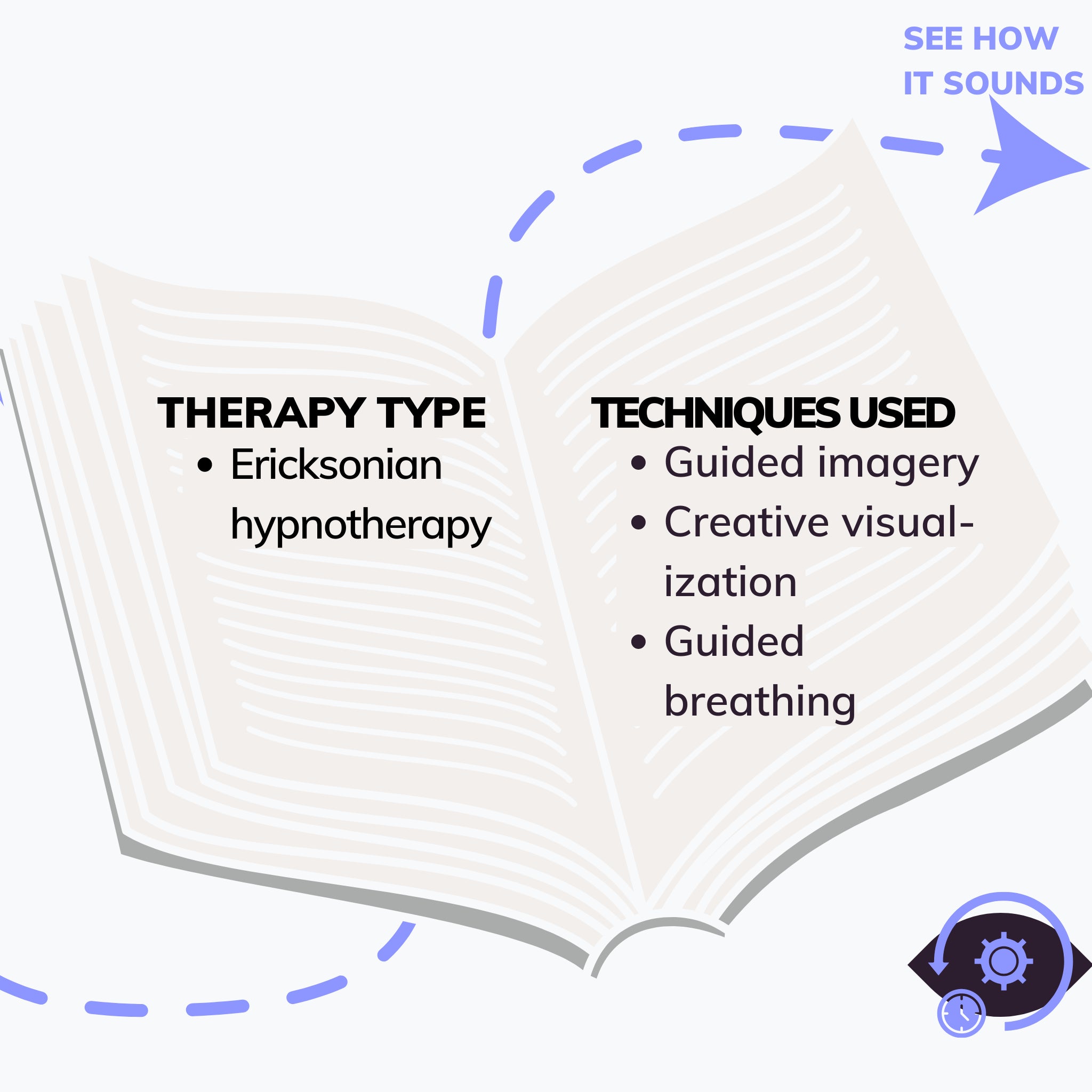
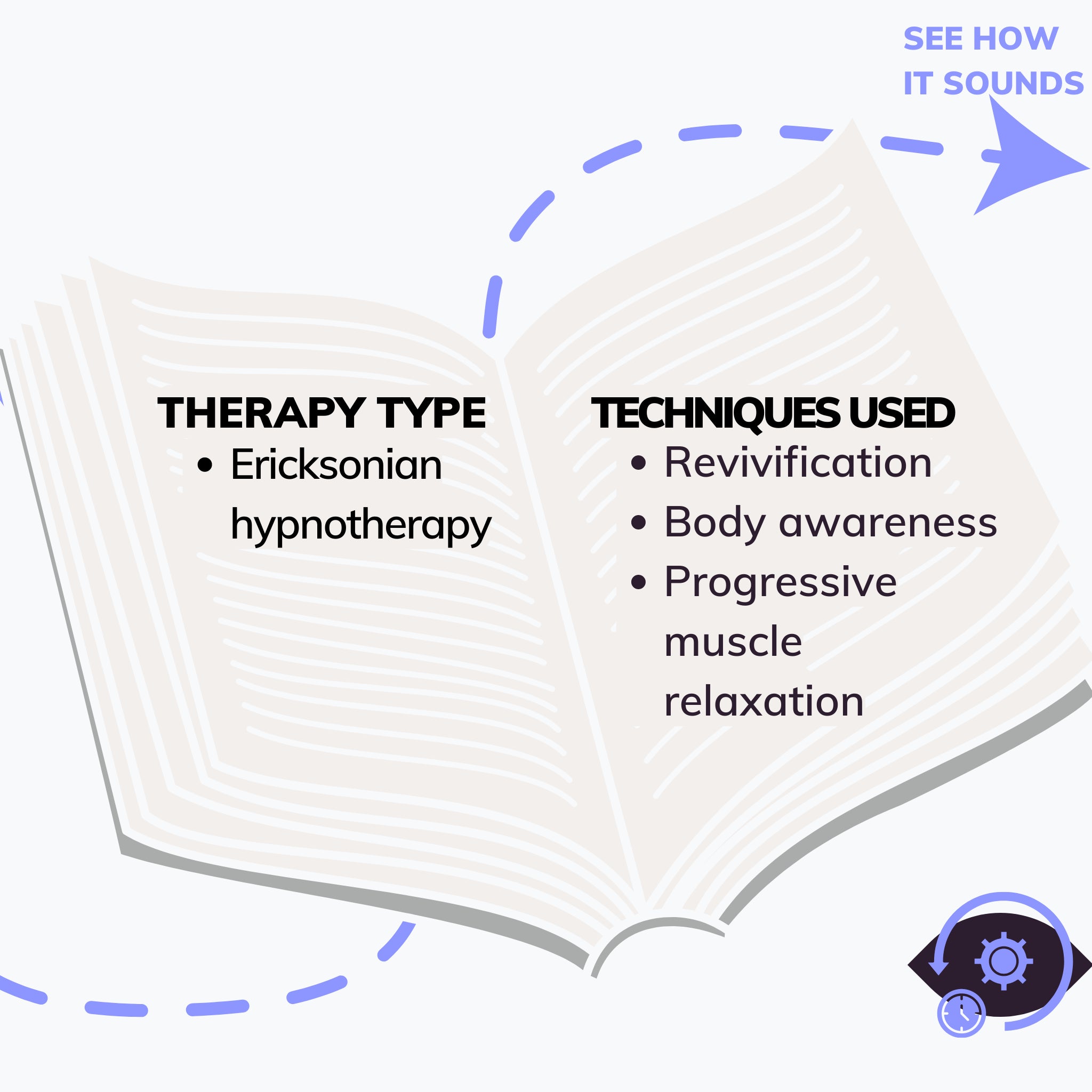
Self Confidence, one of our audio programs, is based on influencing your confidence level. The heart of this trance is that you can identify and be aware within yourself of an area that can become a source of personal power. Also, you can explore the physical sensation of comfort and create bridges. Thus, you connect with the inner resources and the people around you.








Leave a comment
All comments are moderated before being published.
This site is protected by hCaptcha and the hCaptcha Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.